My subject—organizing ecological revolution—has as its initial premise that we are in the midst of a global environmental crisis of such enormity that the web of life of the entire planet is threatened and with it the future of civilization.
This is no longer a very controversial proposition. To be sure, there are different perceptions about the extent of the challenge that this raises. At one extreme there are those who believe that since these are human problems arising from human causes they are easily solvable. All we need are ingenuity and the will to act. At the other extreme there are those who believe that the world ecology is deteriorating on a scale and with a rapidity beyond our means to control, giving rise to the gloomiest forebodings.
Although often seen as polar opposites these views nonetheless share a common basis. As Paul Sweezy observed they each reflect “the belief that if present trends continue to operate, it is only a matter of time until the human species irredeemably fouls its own nest” (Monthly Review, June 1989).
The more we learn about current environmental trends the more the unsustainability of our present course is brought home to us. Among the warning signs:
- There is now a virtual certainty that the critical threshold of a 2° C (3.6° F) increase in average world temperature above the preindustrial level will soon be crossed due to the buildup of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Scientists believe that climate change at this level will have portentous implications for the world’s ecosystems. The question is no longer whether significant climate change will occur but how great it will be (International Climate Change Task Force, Meeting the Climate Challenge, January 2005, http://www.americanprogress.org).
- There are growing worries in the scientific community that the estimates of the rate of global warming provided by the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), which in its worst case scenario projected increases in average global temperature of up to 5.8° C (10.4° F) by 2100, may prove to be too low. For example, results from the world’s largest climate modeling experiment based in Oxford University in Britain indicate that global warming could increase almost twice as fast as the IPCC has estimated (London Times, January 27, 2005).
- Experiments at the International Rice Institute and elsewhere have led scientists to conclude that with each 1° C (1.8° F) increase in temperature, rice, wheat, and corn yields could drop 10 percent (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, July 6, 2004; Lester Brown, Outgrowing the Earth).
- It is now clear that the world is within a few years of its peak oil production (known as Hubbert’s Peak). The world economy is therefore confronting diminishing and ever more difficult to obtain oil supplies, despite a rapidly increasing demand (Ken Deffeyes, Hubbert’s Peak; David Goodstein, Out of Gas). All of this points to a growing world energy crisis and mounting resource wars.
- The planet is facing global water shortages due to the drawing down of irreplaceable aquifers, which make up the bulk of the world’s fresh water supplies. This poses a threat to global agriculture, which has become a bubble economy based on the unsustainable exploitation of groundwater. One in four people in the world today do not have access to safe water (Bill McKibben, New York Review of Books, September 25, 2003).
- Two thirds of the world’s major fish stocks are currently being fished at or above their capacity. Over the last half-century 90 percent of large predatory fish in the world’s oceans have been eliminated (Worldwatch, Vital Signs 2005).
- The species extinction rate is the highest in 65 million years with the prospect of cascading extinctions as the last remnants of intact ecosystems are removed. Already the extinction rate is approaching 1,000 times the “benchmark” or natural rate (Scientific American, September 2005). Scientists have pinpointed twenty-five hot spots on land that account for 44 percent of all vascular plant species and 35 percent of all species in four vertebrate groups, while taking up only 1.4 percent of the world’s land surface. All of these hot spots are now threatened with rapid annihilation due to human causes (Nature, February 24, 2000).
- According to a study published by the National Academy of Sciences in 2002, the world economy exceeded the earth’s regenerative capacity in 1980 and by 1999 had gone beyond it by as much as 20 percent. This means, according to the study’s authors, that “it would require 1.2 earths, or one earth for 1.2 years, to regenerate what humanity used in 1999” (Matthis Wackernagel, et. al, “Tracking the Ecological Overshoot of the Human Economy,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, July 9, 2002).
- The question of the ecological collapse of past civilizations from Easter Island to the Mayans is now increasingly seen as extending to today’s world capitalist system. This view, long held by environmentalists, has recently been popularized by Jared Diamond in his book Collapse.
These and other warning bells indicate that the present human relation to the environment is no longer supportable. The most developed capitalist countries have the largest per capita ecological footprints, demonstrating that the entire course of world capitalist development at present represents a dead end.
The main response of the ruling capitalist class when confronted with the growing environmental challenge is to “fiddle while Rome burns.” To the extent that it has a strategy, it is to rely on revolutionizing the forces of production, i.e., on technical change, while keeping the existing system of social relations intact. It was Karl Marx who first pointed in The Communist Manifesto to “the constant revolutionizing of production” as a distinguishing feature of capitalist society. Today’s vested interests are counting on this built-in process of revolutionary technological change coupled with the proverbial magic of the market to solve the environmental problem when and where this becomes necessary.
In stark contrast, many environmentalists now believe that technological revolution alone will be insufficient to solve the problem and that a more far-reaching social revolution aimed at transforming the present mode of production is required.
Historically addressing this question of the ecological transformation of society means that we need to ascertain: (1) where the world capitalist system is heading at present, (2) the extent to which it can alter its course by technological or other means in response to today’s converging ecological and social crises, and (3) the historical alternatives to the existing system. The most ambitious attempt thus far to carry out such a broad assessment has come from the Global Scenario Group (http://www.gsg.org), a project launched in 1995 by the Stockholm Environmental Institute to examine the transition to global sustainability. The Global Scenario Group has issued three reports—Branch Points (1997), Bending the Curve (1998), and their culminating study, Great Transition (2002). In what follows I will focus on the last of these reports, the Great Transition.*
As its name suggests, the Global Scenario Group employs alternative scenarios to explore possible paths that society caught in a crisis of ecological sustainability might take. Their culminating report presents three classes of scenarios: Conventional Worlds, Barbarization, and Great Transitions. Each of these contains two variants. Conventional Worlds consists of Market Forces and Policy Reform. Barbarization manifests itself in the forms of Breakdown and Fortress World. Great Transitions is broken down into Eco-communalism and the New Sustainability Paradigm. Each scenario is associated with different thinkers: Market Forces with Adam Smith; Policy Reform with John Maynard Keynes and the authors of the 1987 Brundtland Commission report; Breakdown with Thomas Malthus; Fortress World with Thomas Hobbes; Eco-communalism with William Morris, Mahatma Gandhi, and E. F. Schumacher; and the New Sustainability Paradigm with John Stuart Mill.
Within the Conventional Worlds scenarios Market Forces stands for naked capitalism or neoliberalism. It represents, in the words of the Great Transition report, “the firestorm of capitalist expansion.” Market Forces is an unfettered capitalist world order geared to the accumulation of capital and rapid economic growth without regard to social or ecological costs. The principal problem raised by this scenario is its rapacious relation to humanity and the earth.
The drive to amass capital that is central to a Market Forces regime is best captured by Marx’s general formula of capital (though not referred to in the Great Transition report itself). In a society of simple commodity production (an abstract conception referring to pre-capitalist economic formations in which money and the market play a subsidiary role), the circuit of commodities and money exists in a form, C–M–C, in which distinct commodities or use values constitute the end points of the economic process. A commodity C embodying a definite use value is sold for money M which is used to purchase a different commodity C. Each such circuit is completed with the consumption of a use value.
In the case of capitalism, or generalized commodity production, however, the circuit of money and commodities begins and ends with money, or M–C–M. Moreover, since money is merely a quantitative relationship such an exchange would have no meaning if the same amount of money were acquired at the end of the process as exchanged in the beginning, so the general formula for capital in reality takes the form of M–C–M´, where M´ equals M + 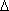
The motor force behind this drive to accumulation is competition. The competitive struggle ensures that each capital or firm must grow and hence must reinvest its “earnings” in order to survive.
Such a system tends toward exponential growth punctuated by crises or temporary interruptions in the accumulation process. The pressures placed on the natural environment are immense and will lessen only with the weakening and cessation of capitalism itself. During the last half-century the world economy has grown more than seven-fold while the biosphere’s capacity to support such expansion has if anything diminished due to human ecological depredations (Lester Brown, Outgrowing the Earth).
The main assumption of those who advocate a Market Forces solution to the environmental problem is that it will lead to increasing efficiency in the consumption of environmental inputs by means of technological revolution and continual market adjustments. Use of energy, water, and other natural resources will decrease per unit of economic output. This is often referred to as “dematerialization.” However, the central implication of this argument is false. Dematerialization, to the extent that it can be said to exist, has been shown to be a much weaker tendency than M–C–M´. As the Global Transition report puts it, “The ‘growth effect’ outpaces the ‘efficiency effect.’”
This can be understood concretely in terms of what has been called the Jevons Paradox, named after William Stanley Jevons who published The Coal Question in 1865. Jevons, one of the founders of neoclassical economics, explained that improvements in steam engines that decreased the use of coal per unit of output also served to increase the scale of production as more and bigger factories were built. Hence, increased efficiency in the use of coal had the paradoxical effect of expanding aggregate coal consumption.
The perils of the Market Forces model are clearly visible in the environmental depredations during the two centuries since the advent of industrial capitalism, and especially in the last half-century. “Rather than abating” under a Market Forces regime, the Great Transition report declares, “the unsustainable process of environmental degradation that we observe in today’s world would [continue to] intensify. The danger of crossing critical thresholds in global systems would increase, triggering events that would radically transform the planet’s climate and ecosystems.” Although it is “the tacit ideology” of most international institutions, Market Forces leads inexorably to ecological and social disaster and even collapse. The continuation of “‘business-as-usual’ is a utopian fantasy.”
A far more rational basis for hope, the report contends, is found in the Policy Reform scenario. “The essence of the scenario is the emergence of the political will for gradually bending the curve of development toward a comprehensive set of sustainability targets,” including peace, human rights, economic development, and environmental quality. This is essentially the Global Keynesian strategy advocated by the Brundtland Commission Report in the late 1980s—an expansion of the welfare state, now conceived as an environmental welfare state, to the entire world. It represents the promise of what environmental sociologists call “ecological modernization.”
The Policy Reform approach is prefigured in various international agreements such as the Kyoto Protocol on global warming and the environmental reform measures advanced by the earth summits in Rio in 1992 and Johannesburg in 2002. Policy Reform would seek to decrease world inequality and poverty through foreign aid programs emanating from the rich countries and international institutions. It would promote environmental best practices through state-induced market incentives. Yet, despite the potential for limited ecological modernization, the realities of capitalism, the Great Transition report contends, would collide with Policy Reform. This is because Policy Reform remains a Conventional Worlds scenario—one in which the underlying values, lifestyles, and structures of the capitalist system endure. “The logic of sustainability and the logic of the global market are in tension. The correlation between the accumulation of wealth and the concentration of power erodes the political basis for a transition.” Under these circumstances the “lure of the God of Mammon and the Almighty dollar” will prevail.
The failure of both of the Conventional Worlds scenarios to alleviate the problem of ecological decline means that Barbarization threatens: either Breakdown or the Fortress World. Breakdown is self-explanatory and to be avoided at all costs. The Fortress World emerges when “powerful regional and international actors comprehend the perilous forces leading to Breakdown” and are able to guard their own interests sufficiently to create “protected enclaves.” Fortress World is a planetary apartheid system, gated and maintained by force, in which the gap between global rich and global poor constantly widens and the differential access to environmental resources and amenities increases sharply. It consists of “bubbles of privilege amidst oceans of misery….The elite[s] have halted barbarism at their gates and enforced a kind of environmental management and uneasy stability.” The general state of the planetary environment, however, would continue to deteriorate in this scenario leading either to a complete ecological Breakdown or to the achievement through revolutionary struggle of a more egalitarian society, such as Eco-communalism.
This description of the Fortress World is remarkably similar to the scenario released in the 2003 Pentagon report, Abrupt Climate Change and its Implications for United States National Security (see “The Pentagon and Climate Change,” Monthly Review, May 2004). The Pentagon report envisioned a possible shutdown due to global warming of the thermohaline circulation warming the North Atlantic, throwing Europe and North America into Siberia-like conditions. Under such unlikely but plausible circumstances relatively well-off populations, including those in the United States, are pictured as building “defensive fortresses” around themselves to keep masses of would-be immigrants out. Military confrontations over scarce resources intensify.
Arguably naked capitalism and resource wars are already propelling the world in this direction at present, though without a cause as immediately earth-shaking as abrupt climate change. With the advent of the War of Terror, unleashed by the United States against one country after another since September 11, 2001, an “Empire of Barbarism” is making its presence felt (Monthly Review, December 2004).
Still, from the standpoint of the Global Scenario Group, the Barbarization scenarios are there simply to warn us of the worst possible dangers of ecological and social decline. A Great Transition, it is argued, is necessary if Barbarization is to be avoided.
Theoretically, there are two Great Transitions scenarios envisioned by the Global Scenario Group: Eco-communalism and the New Sustainability Paradigm. Yet Eco-communalism is never discussed in any detail, on the grounds that for this kind of transformation to come about it would be necessary for world society first to pass through Barbarization. The social revolution of Eco-communalism is seen, by the Global Scenario Group authors, as lying on the other side of Jack London’s Iron Heel. The discussion of Great Transition is thus confined to the New Sustainability Paradigm.
The essence of the New Sustainability Paradigm is that of a radical ecological transformation that goes against unbridled “capitalist hegemony” but stops short of full social revolution. It is to be carried out primarily through changes in values and lifestyles rather than transformation of social structures. Advances in environmental technology and policy that began with the Policy Reform scenario, but that were unable to propel sufficient environmental change due to the dominance of acquisitive norms, are here supplemented by a “lifestyle wedge.”
In the explicitly utopian scenario of the New Sustainability Paradigm the United Nations is transformed into the “World Union,” a true “global federation.” Globalization has become “civilized.” The world market is fully integrated and harnessed for equality and sustainability not just wealth generation. The War on Terrorism has resulted in the defeat of the terrorists. Civil society, represented by non-governmental organizations (NGOs), plays a leading role in society at both the national and global levels. Voting is electronic. Poverty is eradicated. Typical inequality has decreased to a 2–3:1 gap between the top 20 percent and bottom 20 percent of society. Dematerialization is real, as is the polluter pays principle. Advertising is nowhere to be seen. There has been a transition to a solar economy. The long commute from where people live to where they work is a thing of the past; instead there are “integrated settlements” that place home, work, retail shops, and leisure outlets in close proximity to each other. The giant corporations have become forward-looking societal organizations, rather than simply private entities. They are no longer concerned exclusively with the economic bottom line but have revised this “to include social equity and environmental sustainability, not only as a means to profit, but as ends.”
Four agents of change are said to have combined to bring all of this about: (1) giant transnational corporations, (2) intergovernmental organizations such as the United Nations, World Bank, International Monetary Fund, and World Trade Organization, (3) civil society acting through NGOs, and (4) a globally aware, environmentally-conscious, democratically organized world population.
Underpinning this economically is the notion of a stationary state, as depicted by Mill in his Principles of Political Economy (1848) and advanced today by the ecological economist Herman Daly. Most classical economists—including Adam Smith, David Ricardo, Thomas Malthus, and Karl Marx—saw the specter of a stationary state as presaging the demise of the bourgeois political economy. In contrast, Mill, who Marx (in the afterword to the second German edition of Capital) accused of a “shallow syncretism,” saw the stationary state as somehow compatible with existing productive relations, requiring only changes in distribution. In the New Sustainability Paradigm scenario, which takes Mill’s view of the stationary state as its inspiration, the basic institutions of capitalism remain intact, as do the fundamental relations of power, but a shift in lifestyle and consumer orientation mean that the economy is no longer geared to economic growth and the enlargement of profits, but to efficiency, equity, and qualitative improvements in life. A capitalist society formerly driven to expanded reproduction through investment of surplus product (or surplus value) has been replaced with a system of simple reproduction (Mill’s stationary state), in which the surplus is consumed rather than invested. The vision is one of a cultural revolution supplementing technological revolution, radically changing the ecological and social landscape of capitalist society, without fundamentally altering the productive, property, and power relations that define the system.
In my view, there are both logical and historical problems with this projection. It combines the weakest elements of utopian thinking (weaving a future out of mere hopes and wishes—see Bertell Ollman, “The Utopian Vision of the Future,” Monthly Review, July-August 2005) with a “practical” desire to avoid a sharp break with the existing system. The failure of the Global Scenario Group to address its own scenario of Eco-communalism is part and parcel of this perspective, which seeks to elude the question of the more thoroughgoing social transformation that a genuine Great Transition would require.
The result is a vision of the future that is contradictory to an extreme. Private corporations are institutions with one and only one purpose: the pursuit of profit. The idea of turning them to entirely different and opposing social ends is reminiscent of the long-abandoned notions of the “soulful corporation” that emerged for a short time in the 1950s and then vanished in the harsh light of reality. Many changes associated with the New Sustainability Paradigm would require a class revolution to bring about. Yet, this is excluded from the scenario itself. Instead the Global Scenario Group authors engage in a kind of magical thinking—denying that fundamental changes in the relations of production must accompany (and sometimes even precede) changes in values. No less than in the case of the Policy Reform Scenario—as pointed out in The Great Transition report itself—the “God of Mammon” will inevitably overwhelm a value-based Great Transition that seeks to escape the challenge of the revolutionary transformation of the whole society.
Put simply, my argument is that a global ecological revolution worthy of the name can only occur as part of a larger social—and I would insist, socialist—revolution. Such a revolution, were it to generate the conditions of equality, sustainability, and human freedom worthy of a genuine Great Transition, would necessarily draw its major impetus from the struggles of working populations and communities at the bottom of the global capitalist hierarchy. It would demand, as Marx insisted, that the associated producers rationally regulate the human metabolic relation with nature. It would see wealth and human development in radically different terms than capitalist society.
In conceiving such a social and ecological revolution, we can derive inspiration, as Marx did, from the ancient Epicurean concept of “natural wealth.”* As Epicurus observed in his Principal Doctrines, “Natural wealth is both limited and easily obtainable; the riches of idle fancies go on forever.” It is the unnatural, unlimited character of such alienated wealth that is the problem. Similarly, in what has become known as the Vatican Sayings, Epicurus stated: “When measured by the natural purpose of life, poverty is great wealth; limitless wealth is great poverty.” Free human development, arising in a climate of natural limitation and sustainability is the true basis of wealth, of a rich, many-sided existence; the unbounded, pursuit of wealth is the primary source of human impoverishment and suffering. Needless to say, such a concern with natural well-being, as opposed to artificial needs and stimulants, is the antithesis of capitalist society and the precondition of a sustainable human community.
A Great Transition therefore must have the characteristics implied by the Global Scenario Group’s neglected scenario: Eco-communalism. It must take its inspiration from William Morris, one of the most original and ecological followers of Karl Marx, from Gandhi, and from other radical, revolutionary and materialist figures, including Marx himself, stretching as far back as Epicurus. The goal must be the creation of sustainable communities geared to the development of human needs and powers, removed from the all-consuming drive to accumulate wealth (capital).
As Marx wrote, the new system “starts with the self-government of the communities” (Marx and Engels, Collected Works, vol. 24, p. 519; Paul Burkett, “Marx’s Vision of Sustainable Human Development” in this issue). The creation of an ecological civilization requires a social revolution; one that, as Roy Morrison explains, needs to be organized democratically from below: “community by community…region by region” (Ecological Democracy). It must put the provision of basic human needs—clean air, unpolluted water, safe food, adequate sanitation, social transport, and universal health care and education, all of which require a sustainable relation to the earth—ahead of all other needs and wants. Such a revolutionary turn in human affairs may seem improbable. But the continuation of the present capitalist system for any length of time will prove impossible—if human civilization and the web of life as we know it are to be sustained.
Notes
* The authors of the Global Scenario Group’s Great Transition report are Paul Raskin, Tariq Banuri, Gilberto Gallopín, Pablo Gutman, Al Hammond, Robert Kates, and Rob Swart.
* Much of Marx’s analysis in Capital is concerned with where )m or surplus value comes from. To answer this question, he argues, it is necessary to go beneath the process of exchange and to explore the hidden recesses of capitalist production—where it is revealed that the source of surplus value is to be found in the process of class exploitation.
* On Marx’s relation to Epicurus see John Bellamy Foster, Marx’s Ecology (New York: Monthly Review Press, 2000).
Comments are closed.