
No Empires, No Dust Bowls
When scientists describe the increase of Dust Bowl-like conditions under climate change, they signal a particular kind of violent ecological and social change. But equally violent are the social forces, historical developments, policies, and practices that produce such massive socioecological crises in the first place. | more…

Cesspools, Sewage, and Social Murder
The accumulation of human excrement in nineteenth-century cities, particularly London, precipitated a historic environmental crisis—an aspect of the metabolic rift mostly overlooked in ecosocialist analysis. The solution that was finally adopted only shifted the problem out of sight, setting the stage for even greater crises in our time. | more…
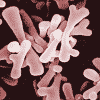
Metabolic Rift and the Human Microbiome
Metabolic rift theory can deepen our understanding of the human microbiota—organisms living on and inside of humans—and the ways that capitalism has disrupted these microbial ecosystems, with serious consequences for our health. | more…

Land–Sea Ecological Rifts
Increasing rates of nitrogen and phosphorus application have caused severe damage to aquatic systems, as rivers, streams, lakes, bays, and ocean systems have been inundated with nutrient runoff. Only by addressing the metabolic rupture in the soil nutrient cycle and the contradictions of capital can we begin to mend these land–sea rifts. | more…

Marx, Value, and Nature
In recent years ecological critiques of capitalism have deepened and multiplied, resulting in new debates over the conception, scope, and purpose of Marx’s value theory and its relation to the natural world. | more…

On English Farming and Sewers
If the British people do not take the pains to secure the natural conditions of the permanent fertility of their land, if they allow these conditions as hitherto to be squandered, their fields will at no distant day cease to yield their returns of corn and meat. | more…

1862 Preface to Agricultural Chemistry
I have had abundant opportunity of estimating the impediments which stand in the way of scientific doctrines passing into the domain of practical Agriculture. The reason of which is, especially, that no connexion was formed between Practice and Science. | more…

June 2018 (Volume 70, Number 2)
With the eruption in March of the scandal around Cambridge Analytica and Facebook, articles raising the alarm on “surveillance capitalism” are suddenly everywhere. The term, which was coined in MR in August of 2014, was developed to highlight the links between digital spying systems and contemporary capitalism as a whole. Academic interpretations of the concept effectively divorced surveillance capitalism from class analysis, and from the overall political-economic structure of capitalism—as if surveillance could be abstracted from monopoly-finance capital as a whole. | more…

The Politics of Food in Venezuela
Few countries and political processes have been subject to such scrutiny, yet so generally misunderstood, as Venezuela and the Bolivarian Revolution. This is particularly true today, as the international media paints an image of absolute devastation in the country, wrought by failed policies and government mismanagement. One way to comprehend the complexities of what is happening in Venezuela today—missed entirely by the dominant, mainstream narrative—is by homing in on the dynamics around Venezuela’s most highly consumed staple foods. | more…

The Birth of the Cuban Polyclinic
During the 1960s, Cuban medicine experienced changes as tumultuous as the civil rights and antiwar protests in the United States. While activists, workers, and students in western Europe and the United States confronted existing institutions of capitalism and imperialism, Cuba faced the even greater challenge of building a new society. | more…

The China–Pakistan Economic Corridor
Three hundred years after what became known in the nineteenth century as the Great Game—a struggle for regional hegemony between the British and Russian Empires—Southwest Asia remains an imperial staging ground. The U.S. invasion of Afghanistan in September 2001 signaled Washington’s desire to cement its hegemonic position, but seventeen years later it is mired in an unwinnable war, even as the U.S. economy—and that of much of the Western world—endures the “endless crisis” of contemporary capitalism. | more…

A Marxist Correspondence
Paul A. Baran (1910–1964) and Paul M. Sweezy (1910–2004) were two of the most creative and influential Marxist economists of the last century. The Age of Monopoly Capital collects hundreds of letters between Baran and Sweezy, written between 1949 and Baran’s death in 1964. The correspondence contains numerous interesting, important, and unanticipated ideas. Nuggets of wisdom about economic theory, socialist history, dialectical method, academic politics, and many other topics are scattered throughout. | more…

Two Intellectual Giants of the American Left
Instead of theory, early U.S. radicals excelled in reportage, like John Reed’s Ten Days That Shook the World, or fiction, like Upton Sinclair’s packing-house shocker The Jungle. To Europeans American thought seemed impermeable to the difficult ideas of Marxism. That changed with the founding of Monthly Review in 1949, which marked a newly realized if not entirely new trend in American Marxist thought. | more…