Volume 64, Issue 11 (April)

One of the achievements of Roosevelt’s New Deal administration during the Great Depression was the introduction in 1938 of the federal minimum wage, then set at twenty-five cents an hour. At no time in its history has the minimum wage kept workers out of poverty. But it has helped to stave off the full depths of poverty that would otherwise ensue.… Obama’s proposal in his State of the Union Address to raise the federal minimum wage to $9 an hour…has received widespread support from the population. At the same time it has been subjected to severe criticism from key sectors of capital, which have gone into overdrive in pushing their claim that such a raise in the hourly wage of the poorest segments of society would be a devastating “job killer,” increasing unemployment.… If Obama’s proposal were adopted the real minimum wage would still be about $1.50 short of where it was in 1968 at the end of the Johnson administration, forty-five years ago. Yet, this paltry attempt to lift the floor of wages for the poorest workers in the United States—at a time when the annual income of a single parent receiving the minimum wage is well below the federal poverty line for a family of three—is coming under virulent attack from the vested interests. | more…
A historical perspective on the economic stagnation afflicting the United States and the other advanced capitalist economies requires that we go back to the severe downturn of 1974–1975, which marked the end of the post-Second World War prosperity. The dominant interpretation of the mid–1970s recession was that the full employment of the earlier Keynesian era had laid the basis for the crisis by strengthening labor in relation to capital. As a number of prominent left economists, whose outlook did not differ from the mainstream in this respect, put it, the problem was a capitalist class that was “too weak” and a working class that was “too strong.” Empirically, the slump was commonly attributed to a rise in the wage share of income, squeezing profits. This has come to be known as the “profit-squeeze” theory of crisis. | more…
In Marx’s work, no final presentation of his theory of crisis can be found. Instead, there are various approaches to explain crises. In the twentieth century, the starting point for Marxist debates on crisis theory was the third volume of Capital, the manuscript of which was written in 1864–1865. Later, attention was directed towards the theoretical considerations on crisis in the Theories of Surplus-Value, written in the period between 1861 and 1863. Finally, the Grundrisse of 1857–1858 also came into view, which today plays a central role in the understanding of Marx’s crisis theory for numerous authors. Thus, starting with Capital, the debate gradually shifted its attention to earlier texts. With the Marx Engels Gesamtausgabe (MEGA), all of the economic texts written by Marx between the late 1860s and the late 1870s are now available. Along with his letters, these texts allow for an insight into the development of Marx’s theoretical considerations on crisis after 1865. | more…
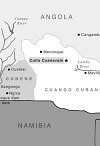
In Angola in the spring of 1988 the armed forces of apartheid South Africa and the US-backed mercenaries of Jonas Savimbi were defeated by the combined force of the Cuban military, the Angolan army, and the military units of the liberation movements of South Africa and Namibia. This led directly to the independence of Namibia and then to the fall of the apartheid regime in South Africa itself. Cuba’s heroic role is the outstanding example of principled anti-imperialist internationalism in the last decades of the twentieth century.… We celebrate the twenty-fifth anniversary of these events by reprinting the account by Horace Campbell that appeared in Monthly Review in April 1989, with some pride at having published so sharp an analysis of current events—events largely ignored by the mass media then and since. We then present a military-focused historical analysis by Monthly Review Press author Ronnie Kasrils, who had the extraordinary fate to have headed ANC military intelligence in the battle alongside the Cubans, and then to have served for five years as Deputy Minister of Defense in the post-apartheid South African government—in regular contact with officers who had commanded the opposing forces. —The Editors
25th Anniversary of a Historic African Battle
Prohibited from meeting openly by South Africa’s apartheid government, the Seventh Congress of the South African Communist Party was held in Cuba in April 1989. When Jorge Risquet, one of Fidel Castro’s shrewdest and most trusted colleagues, addressed the gathered members, he was greeted with the resounding salutation “Viva Cuito Cuanavale!” For the South African delegates, many who had come from military duty in Angola itself where the African National Congress (ANC) had military training facilities courtesy of the government, there was no doubt whatsoever that an epic victory had been recently won at the remote town of Cuito Cuanavale in Angola. The loser was the apartheid military machine in that embattled country in March 1988, constituting a historic turning point in the struggle for the total liberation of the region from racist rule and aggression. | more…
When confronted with any big decision in life, I hear my mom’s voice telling me to listen to my gut. This has worked for personal adventures ranging from backpacking to parenting, even though at times it can be hard to quiet the social noise that prevents us from “hearing” what our instincts have to say. In Greed to Green, Charles Derber explores a new twist on the familiar “listen to your gut” adage by framing climate change inaction as the collective problem of not having a gut feeling about this planetary threat. Rather, he explains that we as a society have cordoned off knowledge of climate change as an intellectual concept, and have not allowed it to migrate to the realm of the gut truth. | more…
Maximilian Forte, Slouching Towards Sirte (Montreal: Baraka Books, 2012), 341 pages, $27.95, paperback.
Perhaps no war in recent memory has so thoroughly flummoxed the Euro-Atlantic left as the recent NATO war on Libya. Presaging what would occur as U.S. proxies carried out an assault on Syria, both a pro-war left and an anti-anti-war left [gave] endless explanations and tortuous justifications for why a small invasion, perhaps just a “no-fly-zone,” would be okay—so long as it didn’t grow into a larger intervention. They cracked open the door to imperialism, with the understanding that it would be watched very carefully so as to make sure that no more of it would be allowed in than was necessary to carry out its mission. The absurdity of this posture became clear when NATO immediately expanded its mandate and bombed much of Libya to smithereens, with the help of on-the-ground militia, embraced as revolutionaries by those who should have known better—and according to Maximilian Forte, could have known better, had they only looked. | more…
The name “Walter Rodney” has receded from public memory in the last few decades. Only yesterday, it seems to this reviewer, Rodney was the most promising young political scholar of Afro-Caribbean origin, influential from parts of Africa to Britain and North America, not to mention his home Guyana, as well as Jamaica, Trinidad, and other anglophone islands. He was revered: great things were expected of him, as great things were expected of the new phase of regional history in which independence had been achieved and masses mobilized for real change. | more…

