Marxism

In this exhilarating graphic novel about the Spanish Civil War, three American friends set off from Brooklyn to join in the fight—determined to make Spain “the tomb of fascism” for the sake of us all. Together they defy the U.S. government and join the legendary Abraham Lincoln Brigade, throw themselves into battle, and conduct sabotage missions behind enemy lines. As Spain is shattered by the savagery of combat during the Spanish Civil War (1936-1939), readers see the darkening clouds of the World War to come. | more…

More than twenty years after the publication of John Bellamy Foster’s Marx’s Ecology (2000), ecosocialist scholars continue to explore the evolution of Marx’s ecological thinking, from the Greek atomists to his later work on ethnology. | more…

John Bellamy Foster’s recent work, The Return of Nature, makes a strong case that Marxism’s central, materialist conception of nature and history makes it the best possible theoretical basis for radical ecological scholarship. | more…

Recent scholarship suggests that the widespread perception of Soviet states as uniquely ecologically disastrous is, at best, exaggerated, and that these environmental legacies must be re-examined. | more…

Over the last 11,700 years, during which human civilization developed, the earth has existed within what geologists refer to as the Holocene Epoch. Now science is telling us that the Holocene Epoch in the geological time scale ended, replaced by a new more dangerous Anthropocene Epoch, which began around 1950. The onset of the Anthropocene Epoch is characterized by an “anthropogenic rift” in the biological cycles of the Earth System, marking a changed reality in which human activities are now the main geological force impacting the earth as a whole, generating at the same time an existential crisis for the world’s population. | more…

Finally, and for the first time, we have full access to a representative collection of Anne Braden’s writings, speeches, and letters, and the full spectrum of their subject matter: from the relationship between race and capitalism, to the role of the South in American society, to the function of anti-communism. | more…

Between 1949 and 1980, over a hundred articles in Monthly Review dealt with the Soviet Union directly, with many more addressing it indirectly. But, after 1993, treatments of post-Soviet Russia in the magazine largely ceased. | more…

Time is running out for humanity to avoid a catastrophic planetary tipping point. Widespread mass mobilizations of populations worldwide must fight to bring about revolutionary societal changes and dismantle neoliberal monopoly capitalism, with its reliance on extractive exploitation of our planet’s resources and communities. | more…
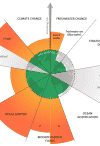
A major deficiency of the growth-obsessed model driving global neoliberal economic policy is its lack of understanding on the Earth System on which it—and indeed, all life on Earth—relies. | more…

Contradicting previous liberal notions of an “end of history,” humanity is now facing unprecedented threats to our species’ survival, but an environmental proletariat to combat them is emerging. | more…

For most economists, labor is simply a commodity, bought and sold in markets like any other – and what happens after that is not their concern. Individual prospective workers offer their services to individual employers, each acting solely out of self-interest and facing each other as equals. The forces of demand and supply operate so that there is neither a shortage nor a surplus of labor, and, in theory, workers and bosses achieve their respective ends. Michael D. Yates, in Work Work Work: Labor, Alienation, and Class Struggle, offers a vastly different take on the nature of the labor market. | more…

Through this dramatic history by Stefan Heym, we become intimate with the story of the maverick and internationalist Karl Radek, known as the editor of the newspaper of record throughout the Soviet era, Isvestia. Beginning as Lenin’s companion at the dawning of the October Revolution, Radek later became Stalin’s favorite intellectual – only to find himself entangled in the great purges of the late 1930s and scripting his own trial. In this, his last historical novel, Heym reveals Radek as a brilliant Bolshevik journalist and politician who found himself at every turn of the wheel of fate. | more…











