Marxist Ecology

An Ecological Marxist Perspective
How are we to understand the origins and historic significance of the concept of ecological civilization? What is its relation to ecological Marxism? And how does all of this relate to the worldwide revolutionary struggle aimed at transcending our current planetary emergency and protecting what Karl Marx called “the chain of human generations”—along with life in general? | more…

Our current geological time period, characterized by drastic planetary shifts due to anthropogenic climate change, is popularly known as the Anthropocene Epoch. Recent proposals for naming the first age of this epoch highlight capitalism’s central role in the ongoing climate crisis. | more…

More than twenty years after the publication of John Bellamy Foster’s Marx’s Ecology (2000), ecosocialist scholars continue to explore the evolution of Marx’s ecological thinking, from the Greek atomists to his later work on ethnology. | more…

John Bellamy Foster’s recent work, The Return of Nature, makes a strong case that Marxism’s central, materialist conception of nature and history makes it the best possible theoretical basis for radical ecological scholarship. | more…

Over the last 11,700 years, during which human civilization developed, the earth has existed within what geologists refer to as the Holocene Epoch. Now science is telling us that the Holocene Epoch in the geological time scale ended, replaced by a new more dangerous Anthropocene Epoch, which began around 1950. The onset of the Anthropocene Epoch is characterized by an “anthropogenic rift” in the biological cycles of the Earth System, marking a changed reality in which human activities are now the main geological force impacting the earth as a whole, generating at the same time an existential crisis for the world’s population. | more…

Time is running out for humanity to avoid a catastrophic planetary tipping point. Widespread mass mobilizations of populations worldwide must fight to bring about revolutionary societal changes and dismantle neoliberal monopoly capitalism, with its reliance on extractive exploitation of our planet’s resources and communities. | more…
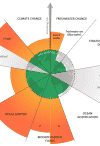
A major deficiency of the growth-obsessed model driving global neoliberal economic policy is its lack of understanding on the Earth System on which it—and indeed, all life on Earth—relies. | more…

The South African climate justice movement presents a model for popular revolt against the ecofascist project. | more…

Contradicting previous liberal notions of an “end of history,” humanity is now facing unprecedented threats to our species’ survival, but an environmental proletariat to combat them is emerging. | more…

The rapid financialization of nature is promoting a Great Expropriation of the global commons and the dispossession of humanity on an unprecedented scale. | more…

Degrowth and ecosocialism are two of the most important movements—and proposals—on the radical side of the ecological spectrum. | more…

From September to November 2021, overlapping with the 2021 UN Climate Change Conference negotiations in Glasgow, three major interrelated developments occurred in global finance. Taken together, these changes mark a turning point in the financial expropriation of the earth and the culmination of a theoretical shift in the dominant economic paradigm aimed at the unlimited accumulation of total capital, which is now seen as including “natural capital.” | more…











