February 1, 2026
In this talk from the inaugural conference of the Society for Peace, Internationalism, and Ecology, John Bellamy Foster relates the story of Prometheus, as presented in the plays of Aeschylus, to Western Marxism's "dialectic of defeat," in which capitalism is portrayed as an unbreakable bond for the working class. Instead, Foster says, we must recognize Prometheus as a subject who is freed from the seemingly inescapable fetters imposed upon him.
February 1, 2026
Speaking before at the Opening Ceremony of the Fourth World Conference on Marxism in Beijing, John Bellamy Foster discusses the development of eco-Marxism and its relation to Marxist theory. Here, Foster argues, "eco-Marxism as we know it today is not simply another branch of Marxism," but is a pathway to the projects of complete socialism and ecological civilization.
February 1, 2026
Paul Buhle reviews
Insectopolis: A Natural History, a new graphic novel by Peter Kuper. In the book, Kuper, a prolific producer and publisher of left-wing comics, spins a tale of two siblings who find themselves in a world of insects. Through encounters with butterflies, beetles, ants, and more, Kuper reveals the deep entanglements between human society—at its best and worst—and the creatures of its living environment.
January 1, 2026
David E. Perlman and Ashly Vigneault explore the linkages between humanity's metabolic rift with nature and the accelerating emergence of epidemics, which are fundamentally related to the capitalist mode of production and concomitant alienated social metabolism. Using historical and epidemiological research that extends from the rise of the bubonic plague to the emergence of COVID-19, Perlman and Vigneault are able to deftly tie these concepts to the breach of planetary boundaries that threatens all of humanity.
January 1, 2026
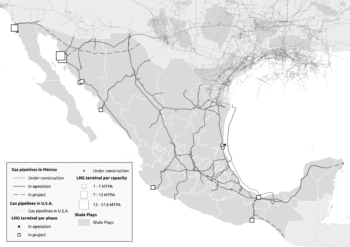
Mateo Crossa delineates the history of U.S. imperialism in Mexico through the lens of its domination of the fossil fuel industry, particularly by way of the Shale Revolution and the advent of fracking. "By engineering new regional dependencies and reshaping energy alliances to suit is strategic ambitions," Crossa writes, "the United States weaponized its command over natural gas to deepen its grip on the global fossil energy system and reinforce its imperial reach."
November 1, 2025
In Aeschylus’s play
Prometheus Bound, the Prometheus is a revolutionary figure. Defying divine interdiction to bring fire to humanity, the Titan has since been adopted by thinkers from the Enlightenment to today to represent revolutionary forces in human existence. So, John Bellamy Foster asks in November’s Review of the Month, what is “Prometheanism,” and how has the term been used (and misused) in discussions of Marx, the ecological crisis, and sustainable human development?
October 1, 2025
In this month's "Note from the Editors,"
MR editors detail importance of understanding the world's grossly unequal carbon emissions output in terms of class while also recognizing the role of imperialism at the center of the crisis. "The rapidly worsening climate conditions threatening the world population," they write, "can thus be seen as a product of the ongoing
class war perpetuated by the 'billionaire class' against working people everywhere."
October 1, 2025
In this interview with Xu Tao and Lv Jiayi, John Bellamy Foster discuss the history and present of ecological Marxism. Foster explores origins of the term
Anthropocene and its predecessors, the concept of degrowth, the continuing influence of metabolic rift theory, and the cutting-edge issues facing young scholars of degrowth today.
October 1, 2025
Ian Angus illuminates the politics behind the decision by the International Union of Geological Sciences not to recognize the Anthropocene as a formal geological epoch. In recounting the debate, Angus explores how the organization undermined the conclusions of top scientists to oppose the establishment of the Anthropocene, and its implications for the public debate about the planetary crisis.
July 1, 2025
This month's "Notes from the Editors" discusses the accelerating progress of China toward sustainability. China's decline in carbon emissions and rapidly decarbonizing energy sector demonstrates the importance of societal realignment and extensive planning to shift toward the ecological modernization that has continued to elude monopoly-capitalist regimes.